Top 15 Data Structures and Algorithm Interview Questions for Java Programmer - Answers
Data structures and algorithm questions are an important part of any programming job interview, be it a Java interview, C++ interview or any other programming language. Since data structures are core programming concepts, it's mandatory for all programmers, to know basic data structures like the stack, linked list, queue, array, tree, and graph. Though trees and graphs are on the tougher side, I still see programmers get familiar will all these. Any list of programming job interview questions is incomplete without questions from data structures and algorithms. Similarly, while going on questions from data structure you may get some programming exercise as well e.g. swapping numbers without temp variable.
The li nked list and array are favorite topics in any data structure interview, questions like reversing a linked list, traversing a linked list or deleting nodes from the linked list, which involves algorithm and data structures that are quite common.
Similarly, finding duplicates in an array, finding missing numbers, sorting arrays are very popular. You can also expect questions from the stack, queue, array, linked list, tree, graph, and hash table are most common in any data structure interview.
In this tutorial, we will see a couple of data structure questions answers from these topics. Let us know if you have any interesting questions from data structures and algorithms, which you faced during any Java interviews.
Btw, you need some understanding of basic data structure before solving these questions. There is no point in attempting these questions if you don't know how to access elements from an array or linked list or can't even code them using the programming language of your choice.
In such cases, it's better to revise fundamentals by joining a comprehensive online course like Data Structures and Algorithms: Deep Dive Using Java . This way you can get the best of both the world, you will learn data structure and algorithms and also prepare for the interview.
15 Data Structures and Algorithm Interview Questions for Java Programmers
 This is a combined list of questions from the various data structures e.g. array, linked list, stack or queue. It includes some coding questions as well, which gel with data structures.
This is a combined list of questions from the various data structures e.g. array, linked list, stack or queue. It includes some coding questions as well, which gel with data structures.
Question 1: How to find middle element of linked list in one pass?
One of the most popular questions from data structures and algorithms mostly asked on a telephonic interview. Since many programmers know that, in order to find the length of a linked list we need to first traverse through the linked list till we find the last node, which is pointing to null, and then in second pass we can find a middle element by traversing only half of length.
They get confused when the interviewer asks him to do the same job in one pass i.e. without traversing the linked list again.
In order to find middle element of linked list in one pass, you need to maintain two-pointer, one increment at each node while other increments after two nodes at a time, by having this arrangement, when the first pointer reaches the end, the second pointer will point to a middle element of the linked list. See this trick to find middle element of linked list in a single pass for more details.
Question 2: How to find if a linked list has a loop?
This question has a bit of similarity with the earlier algorithm and data structure interview question. I mean we can use two pointer approach to solve this problem.
If we maintain two pointers, and we increment one pointer after processing two nodes and other after processing every node, we are likely to find a situation where both the pointers will be pointing to the same node.
This will only happen if a linked list has a loop or cycle. You can check my article linked list with cycles for more details.
Question 3: How to find the third element from the end in a linked list in one pass?
This is another frequently asked linked list interview question. This question is exactly similar to find middle element of linked list in a single pass.
If we apply the same trick of maintaining two-pointers and increment another pointer, when first has moved up to the 3rd element, then when the first pointer reaches the end of the linked list, the second pointer will be pointing to the 3rd element from last in a linked list.
Sometimes, interviewers can also generalize this problem and ask him to find the kth element from the tail, end or last. Just use the same logic, replace 3 with k and you can solve the problem.
If you want to learn more about the linked list, you can also check out Algorithms and Data Structures - Part 1 and 2 courses on Pluralsight.

Btw, you would need a Pluralsight membership to access this course, which costs around $29 monthly or $299 annually. I have one and I also suggest all developers have that plan because Pluralsight is like NetFlix for Software developers.
It has more than 5000+ good quality courses on all the latest topics. Since we programmers have to learn new things every day, an investment of $299 USD is not bad.
Btw, it also offers a 10-day free trial without any obligation which allows you to watch 200 hours of content. You can watch this course for free by signing for that trial.
Question 4: In an integer array, there is 1 to 100 number, out of one is duplicate, how to find?
This is a rather simple data structure question, especially for this kind of. In this case, you can simply add all numbers stored in an array, and the total sum should be equal to n(n+1)/2. Now just subtract actual sum to expected sum, and that is your duplicate number.
Of course, there is a brute force way of checking each number against all other numbers, but that will result in the performance of O(n^2) which is not good.
By the way, this trick will not work if an array has multiple duplicates or its not numbers forming an arithmetic progression. Here is an example of one way to find the duplicate number in the array.
Question 6: How to reverse String in Java?
This is one of my favorite questions. Since String is one of the most important types of programming, you expect a lot of question-related to String any data structure interview.
There are many ways to reverse String in Java or any other programming language, and the interviewer will force you to solve this problem by using without API i.e. without using the reverse() method of StringBuffer.
In the follow-up, he may ask to reverse String using recursion as well. See 3 ways to reverse String in Java to learn to reverse String using both loops and recursion in Java.
Question 7: Write a Java program to sort an array using the Bubble Sort algorithm?
I have always sent a couple of questions from searching and sorting in data structure interviews. Bubble sort is one of the simplest sorting algorithms but if you ask anyone to implement on the spot it gives you an opportunity to gauge the programming skills of a candidate. See How to sort an array using Bubble Sort in Java for a complete solution of this data structure interview question.
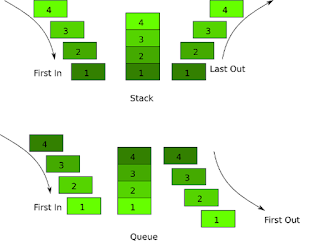
Question 8: What is the difference between Stack and Queue data structure?
One of the classical data structure interviews question. I guess everyone knows, No? Anyway, the main difference is that Stack is LIFO (Last In First Out) data structure while Queue is a FIFO (First In First Out) data structure. You can further see my article stack vs queue in Java for more details.
Question 9: How do you find duplicates in an array if there is more than one duplicate? (solution)
Sometimes this is asked a follow-up question of earlier data structure interview questions, related to finding duplicates in Array. One way of solving this problem is by using a Hashtable or HashMap data structure.
You can traverse through the array, and store each number as key and number of occurrence as value. At the end of traversal, you can find all duplicate numbers, for which occurrence is more than one.
In Java if a number already exists in HashMap then calling get(index) will return number otherwise it returns null. this property can be used to insert or update numbers in HashMap.
Question 10: What is the difference between the Singly Linked List and Doubly Linked List data structure?
This is another classical interview question on the data structure, mostly asked on telephonic rounds. The main difference between the singly linked list and the doubly linked list is the ability to traverse.
In a singly linked list, a node only points towards the next node, and there is no pointer to the previous node, which means you can not traverse back on a singly linked list.
On the other hand, the doubly linked list maintains two pointers, towards the next and previous node, which allows you to navigate in both directions in any linked list.
If you want to learn more about essential data structure, you can also check out JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures Masterclass By Colt Steele.

Question 11: Write a Java program to print the Fibonacci series?
This is not a data structure question, but a programming one, which many times appear during data structure interview. Fibonacci series is a mathematical series, where each number is the sum of the previous two numbers e.g. 1,1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21.
An interviewer is often interested in two things, a function that returns an nth number in the Fibonacci series and solving this problem using recursion in Java.
Though, its easy question, the recursion part often confuses beginners. See this link to find the nth Fibonacci number in Java.
Question 12: Write a Java program to check if a number is a palindrome or not? (solution)
This is similar to the previous question, not directly related to data structures, but quite popular along with other questions. A number is called palindrome if the reverse of the number is equal to the number itself.
An interviewer asks to solve this problem without taking help from Java API or any open source library. Anyway, it’s a simple question, you can use the division operator (/) and remainder operator (%) to solve this question.
Just remember, division operator can be used to get rid of the last digit e.g. 1234/10 will give you 123, and modulus operator can give you last digit e.g. 1234%10 will return 4. By the way, here is a Java program check if the number is palindrome or not.
Question 13: What is a binary search tree? (solution)
This is a data structure question from Tree data structures. Binary Search Tree has some special properties e.g. left nodes contain items whose value is less than root, right subtree contains keys with higher node value than root, and there should not be any duplicates in the tree.
Apart from the definition, an interview can ask you to implement a binary search tree in Java and questions on tree traversal e.g. in order, preorder, and postorder traversals are quite popular data structure questions.
Question 14: How to reverse a linked list using recursion and iteration? (solution)
This is another good question on data structures. There are many algorithms to reverse the linked list and you can search for them using google. I am thinking of writing another blog post to explain the linked list reversal and will share it with you later.
As one of my readers mentioned, I have already written about it and linked it into the solution link, you can check out my solution but I strongly suggest you try it yourself before looking at the solution.
Question 15: Write a Java program to implement Stack in Java? (solution)
You can implement Stack by using an array or linked list. This question expects you to implement a standard method provided by stack data structure e.g. push() and pop(). Both push() and pop() should be happening at top of the stack, which you need to keep track of. It’s also good if you can implement utility methods like contains(), isEmpty() etc.
By the way, JDK has a java.util.Stack class and you can check it’s code to get an idea. You can also check theEffective Java book, where Josh Bloch has explains how an incorrect implementation of the stack can cause a memory leak in Java.
I also suggest looking at data structure and algorithm questions on Cracking the Coding Interview book, as this book contains some good questions with proper explanation. That will certainly help you to do better in programming job interviews.

One more suggestion I have to make is whenever you get some time, just read the Introduction to Algorithm by Thomas Cormen , if you have not read already. This book is the bible of algorithms and IMHO every programmer should read this book.
That's all on this list of data structure interview questions and answers. This is one topic, which is always asked in any programming interview, doesn't matter if you are C, C++, or Java developer, basic knowledge of data structure like an array, linked list, stack, queue, tree are must to clear any programming interview.
Further Learning
Data Structures and Algorithms: Deep Dive Using Java
Algorithms and Data Structures - Part 1 and 2
100+ Data Structure and Algorithms Questions for Programmers
10 Algorithm Books Every Programmer Should Read
Top 5 Data Structure and Algorithm Books for Java Developers
10 Courses to Prepare for Programming Job Interviews
Data Structures in Java by Heinz Kabutz (Java Champion)
Thanks a lot for reading this article so far. If you like these Data Structure and Algorithm Interview questions then please share with your friends and colleagues. If you have any questions or feedback then please drop a note.
P. S. - If you think that your data structure and algorithm skill is not par and you want to spend some time to sharpen your skill then you can start with these free Algorithm courses.
Join the conversation